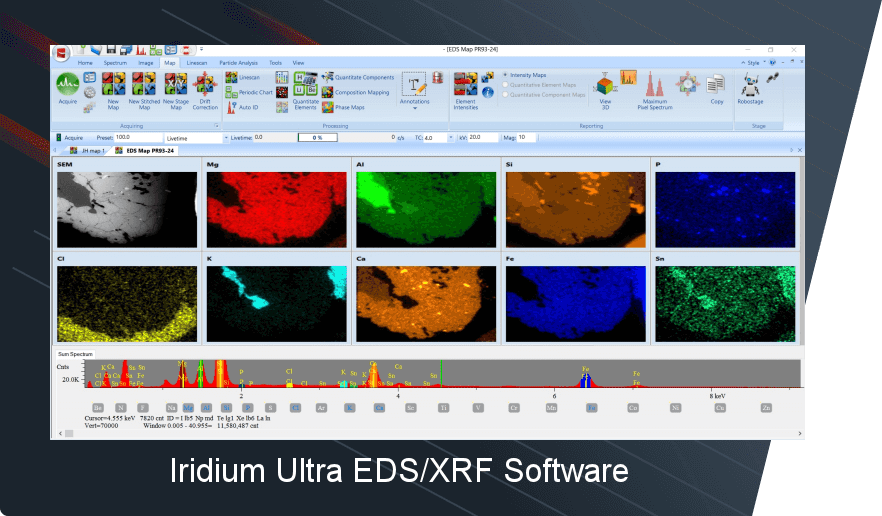
Electronic components are everywhere in our modern world. It is imperative that these components are reliable, as they control extremely important systems from every day items, to electronically controlled military equipment as well as a variety of aerospace equipment. To assure this reliability components must go through a battery of tests. XRF analysis is an irreplaceable tool for the semiconductor industry to not only guarantee but to also certify their products.
Resources
Application Notes
DON’T SEE WHAT YOU ARE LOOKING FOR?


Centerline Segregation in Continuous Casting
Advanced continuously cast high strength low alloy steels are often subject to elemental segregation along the billet or slab centerline during casting and cooling. Monitoring macrosegregation is critical before billet or slab rolling and forming, for if elemental segregation is excessive it can lead to structural weakness, including cracking and breaking of rolled and formed products. Hence, by catching macrosegregation before rolling and forming can save substantially in production costs and material handling and product remelting and casting.

Forensics
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is a very useful and versatile tool to forensic scientists. It is a non-destructive technique, which is particularly advantageous if the sample is limited or further analysis is needed. Not only is it a non-destructive technique, it requires essentially no sample preparation. The ATLAS from IXRF Systems is a small spot µ-XRF unit which is capable of analyzing extremely small samples down to 10 microns or scanning a small area of interest. µ-XRF is especially useful for analyzing trace levels of elements in the ppm range, which can mean differentiation where other techniques falter or it could add to the weight of the evidence by showing samples cannot be differentiated.

Cement
Concrete, in its simplest form, is a mixture of paste and aggregates. The paste, composed of portland cement and water, coats the surface of the fine and coarse aggregates. Through a chemical reaction, the paste hardens and gains strength to form the rock-like mass known as concrete.

Geology
In studying the planetary processes and makeup of the Earth, as well as other bodies in our solar system, geologists routinely analyze the composition of huge variety of materials including: rock, mineral and meteorite samples. Rapid elemental analyses for sodium through uranium at trace levels can be accomplished through X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) instrumentation without destruction, digestion or alteration of the sample. No sample preparation: highly polished samples are not required, and even rough samples can be analyzed with excellent results.

RoHS
The Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) is a compliance directive that holds companies directly responsible for ensuring their electrical and electronic equipment (EEE) conform to strict standards. This directive requires that products cannot contain lead, cadmium, mercury, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs), polybrominated
diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), and four different phthalates above specifically set amounts. These restricted materials are hazardous to the environment and pollute landfills, and are dangerous in terms of occupational exposure during manufacturing and recycling.

Soils
Soil contamination occurs when the amount of elements or chemicals in the soil increase above normal limits as a result of human action. Soil can become contaminated though a huge variety of sources. Contaminated sites often have heavy metals, which are an ill-defined group of inorganic chemical hazards.
Looking for a Specific Application Note?
Fill out the form to request an application note. We have many that are instantly available and others we will customize to your needs.