The journey to understanding human growth and development often leads to unexpected yet fascinating discoveries. Among these is the study of human baby teeth and bones, which provides unique insights into a child’s overall health. Beyond traditional dental or orthopedic research, these tissues are windows into a child’s nutritional and environmental history. A groundbreaking approach to analyzing growth and development involves high-spatial-resolution microXRF, a powerful tool that reveals the elemental composition of teeth and bones with unmatched precision.
This article, brought to you by IXRF Systems, explores how microXRF spectroscopy advances our understanding of biomineralization in teeth and its implications for health research.
What is MicroXRF?
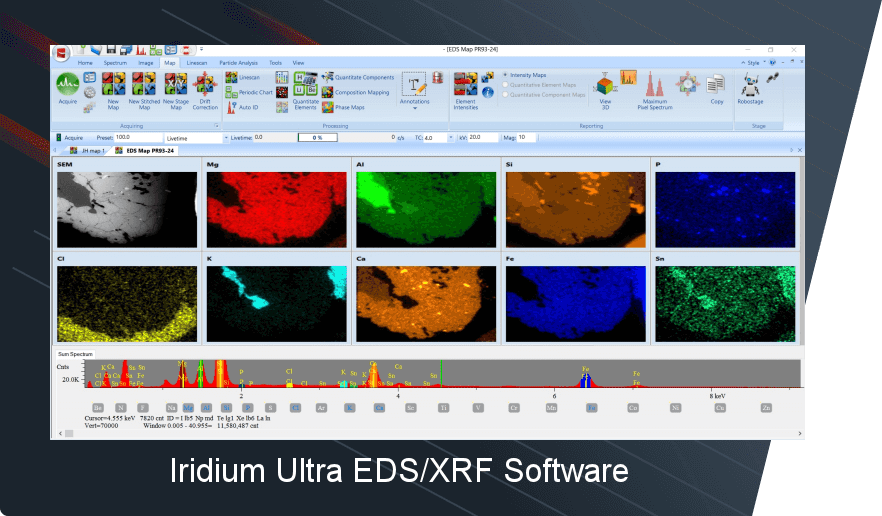
Micro X-ray Fluorescence (microXRF) is a cutting-edge analytical technique that enables nondestructive elemental analysis at a microscopic scale. Unlike traditional XRF, microXRF focuses an ultrafine X-ray beam—as small as 5µm featured on the Atlas series—onto a sample. This interaction excites the sample’s atoms, causing them to emit secondary X-rays unique to each element. This allows researchers to identify and quantify elements with high spatial precision.
MicroXRF is versatile and can analyze solid, tissue, liquid, and powdered samples with minimal preparation. Its applications extend across fields, from materials science to biological research.
MicroXRF for Studying Biomineralization in Teeth and Bones
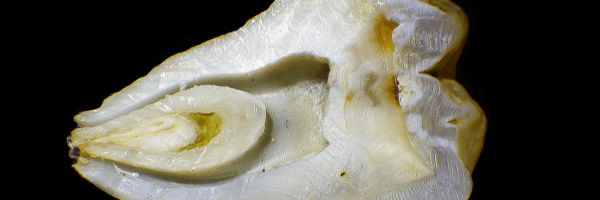
MicroXRF allows for the non-destructive examination of the elemental composition and distribution in teeth and bones. As children grow, trace elements from their environment and diet are integrated into their teeth and bone structures. Just like tree rings, teeth provide a chronological record of exposure to these elements. MicroXRF allows us to analyze tooth development, shedding light on a child’s early life exposures and potential health implications.
Insights Through Elemental Composition and Distribution
The elemental composition of baby teeth (also referred to as primary or milk teeth) and bones hold valuable information about a child’s environmental and nutritional history. This research helps us understand the influence of factors such as diet, environmental toxins, and parental habits like smoking on their growth and development. Certain elements, including lead, arsenic, and mercury, are particularly important to monitor due to their significant health impacts.
Researchers can identify potential associations between early life exposure to certain elements – as determined by microXRF – and subsequent health issues by linking the elemental data with health and development outcomes. This information plays a critical role in formulating public health initiatives to protect children’s health.
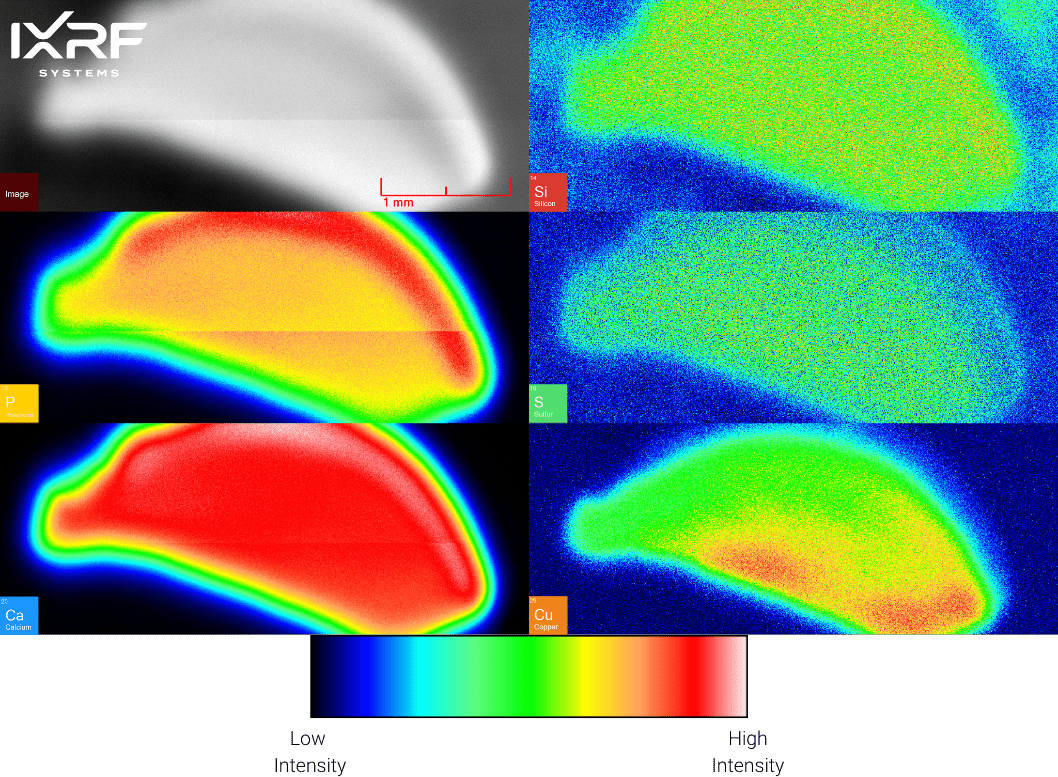
Figure 1: 2D elemental heat maps of a sliced baby incisor tooth ~0.8 mm thick. Maps were collected on the Atlas M microXRF at a pixel size of 5µm.
The Dentin-Enamel Junction (DEJ) – A Crucial Interface
One portion of the tooth that can illuminate developmental differences is the crucial interface between odontoblasts and ameloblasts at the junction where dentin and enamel usually meet and become tightly bound to each other. This interface, also known as the Dentin-Enamel Junction (DEJ), plays a critical role in tooth strength and resilience. The DEJ is the interface between the two primary mineralized tissues of the tooth: enamel, the hardest tissue in the human body, produced by ameloblasts, and dentin, a slightly softer material produced by odontoblasts. This junction is critical for the mechanical integrity of the tooth. Despite the stark difference in the properties of enamel and dentin, they form a seamless connection at the DEJ, giving the tooth its unique combination of hardness and resilience.
How IXRF Systems Supports This Research
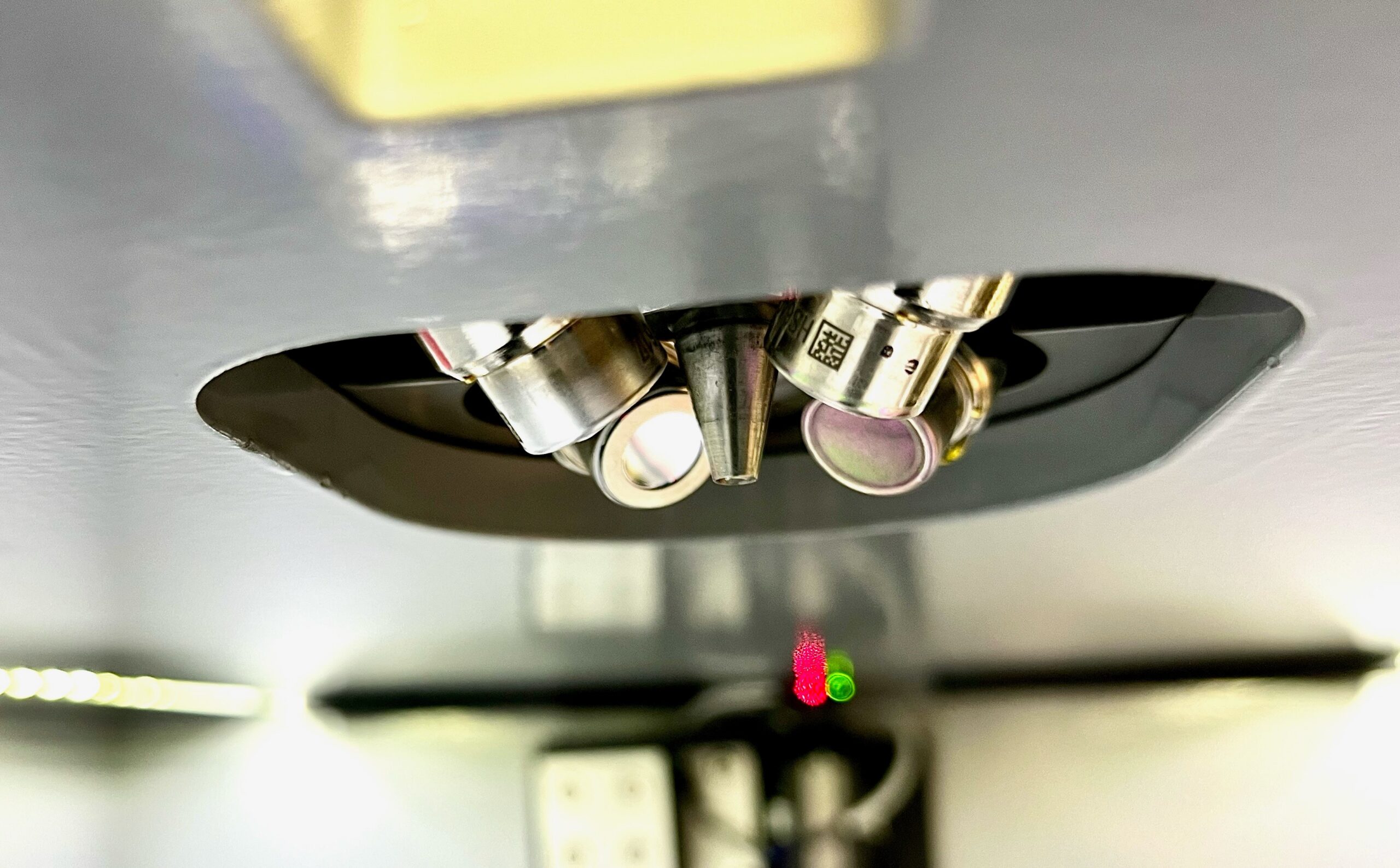
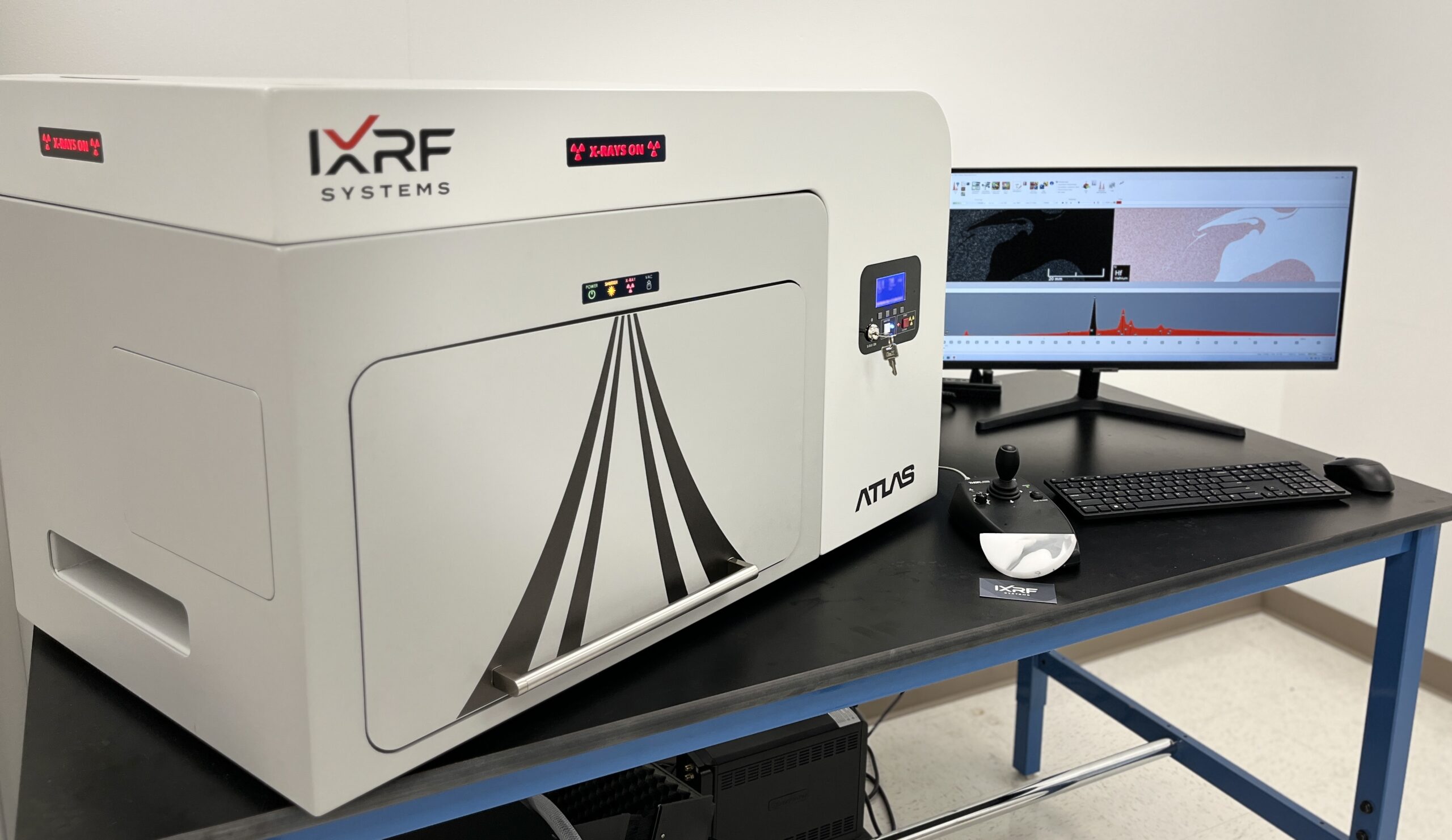
IXRF Systems empowers researchers with state-of-the-art tools like the Atlas series microXRF spectrometers. Featuring spatial resolutions as fine as 5µm and configurations with up to four silicon drift detectors (SDDs), these instruments deliver high-throughput, accurate analyses ideal for biomineralization studies.
Figure 2: Atlas M microXRF spectrometer and its advanced polycapillary X-ray source with four SDDs.
At IXRF Systems, our mission extends beyond technology. We aim to support researchers in unraveling the complexities of human health by collaborating on projects that enhance our understanding of early-life exposures and their impacts.
Why MicroXRF Matters for Healthcare and Beyond
MicroXRF’s ability to map and quantify elemental distributions in teeth and bones has far-reaching implications. From improving dental care and materials to developing interventions for bone-related disorders, the insights gained through this technology could revolutionize healthcare.
Get Started with IXRF Systems
Are you captivated by the intricate process of biomineralization? At IXRF Systems, we offer advanced microXRF technology designed to drive innovation in research. Whether you’re exploring early-life exposures or developing novel dental materials, our tools and expertise are here to help.
Contact us today to learn more about how our microXRF solutions can support your research. Together, we can build a healthier future through science.
IXRF Systems is a leading provider of X-ray fluorescence instrumentation. With our advanced analytical solutions, we are committed to supporting research, quality control, and educational endeavors across various industries.